Fecal Diversion
Fecal diversion is indicated in metastatic colon/rectal cancer or as a bridge to definitive management of conditions such as diverticulitis, pelvic abscess.
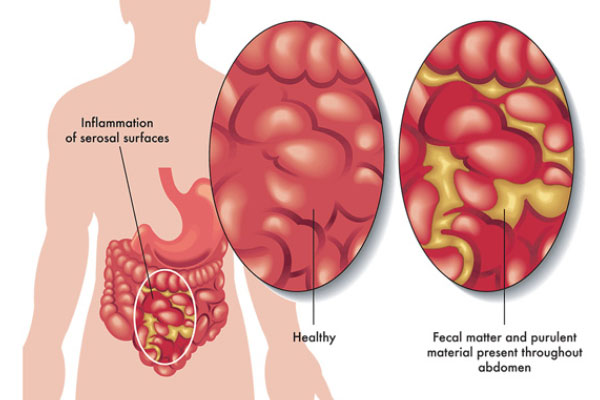
Fecal diversion is indicated in metastatic colon/rectal cancer or as a bridge to definitive management of conditions such as diverticulitis, pelvic abscess.

The colostomy bag is vital in the following clinical conditions:
The procedure is different for the different types of colostomy
There is a high risk of infections as the procedure involves the perforation of the intestinal lumen to fix a colostomy bag. In some of the procedures, the loop of the intestines is exposed to the outside when a stoma is fixed on the abdominal wall.
Bleeding may occur after the procedure.
During the fixing of the colostomy bag, there is a possibility of secondary injuries to other organs of the abdomen.
There is a chance that the fixed colostomy bag may come off the patient or it gets blocked and no longer functions as it is supposed to.
The patient should be assessed if they are fit for the surgical procedure through a comprehensive history and physical examination. Addition lab work is also used to aid this process.
The patient should then be put on prophylactic antibiotics before the surgery to minimize the risk of infections.
Since the operation is on the lumen of the intestines, laxatives are given to clear the lumen of fecal matter in readiness for the colostomy procedure.
The patient should also plan the mode of transport they are going to use after being discharged from the hospital.
The patient is required to have fasted for a minimum of 8-12 hours because of the use of the general anesthesia.
The patient will be discharged home in a few days and therefore should be advised by the nurse in charge on how to handle the colostomy bag before leaving for home.
The patient should be advised on the diet. The main aim is to make sure that the stomach is not greatly distended by uncontrolled eating shortly after surgery; therefore the patient is required to take only small frequent meals to aid the healing process of the stomach
Secondly, unless allergic to protein, the patient is supposed to have a high protein diet because of the healing process. A balanced diet is advised and the protein should be in excess.
The patient should take the medication and the advice given by the doctor such as taking frequent walks to prevent the formation of blood clots which could be potentially fatal. This also includes taking of the blood thinners in the case of prolonged immobilization.
Avoid heavy lifting or any other strenuous exercise until fully healed.
The patient should be fully healed in about 2 months and resuming their normal activities.
Colostomy bags have great outcomes and minimal expected complications. Routine checkups should be made to check the integrity of the colostomy bag especially if a permanent colostomy is placed.