Anal cancer is a rare condition that may produce symptoms such as bleeding from the anus or rectum or a lump that forms in the area. If anal cancer is diagnosed, depending on the stage of the disease, treatment may include radiation, chemotherapy, or surgery.
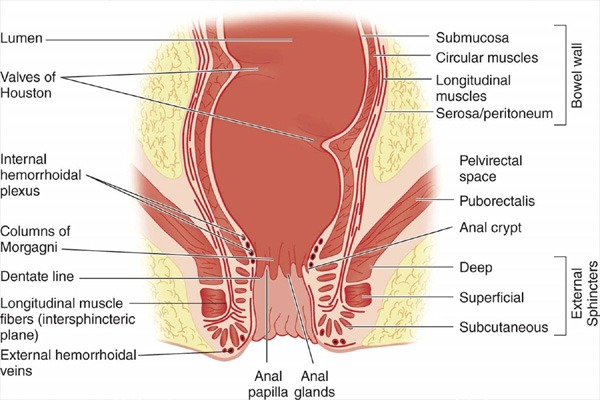
Risks of Developing Anorectal Disorders
While the cause of anal cancer is not always known, there are risks that may increase the chance of developing anal cancer. People infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV) have a greater risk of developing anal cancer, and there is also an increased risk for those who:
- Have many sexual partners
- Are over the age of 50
- Have anal fistula
- Have receptive anal intercourse
- Smoke cigarettes
People with suppressed immune systems or who take medication that suppresses their immune system, are also at risk for developing anal cancer.
Symptoms of Anorectal Disorders
Symptoms of anal cancer include a mass or growth in the anus or rectum as well as:
- Bleeding from the anus or rectum
- Pain or pressure in the anal area
- Discharge from the anus,
- Have receptive anal intercourse
- Anal itching
A change in bowel habits may also be a sign of anal cancer.

