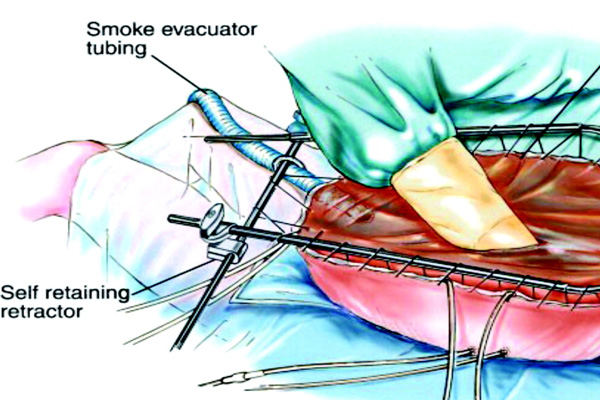
Surgery for Stage IV Colon Cancer (HIPEC)
Colon cancer is one of the most common malignancies of the gastrointestinal system. It occurs more in males than females. The stages of colon cancer run from stage I to stage IV in which stage IV is the most advanced.