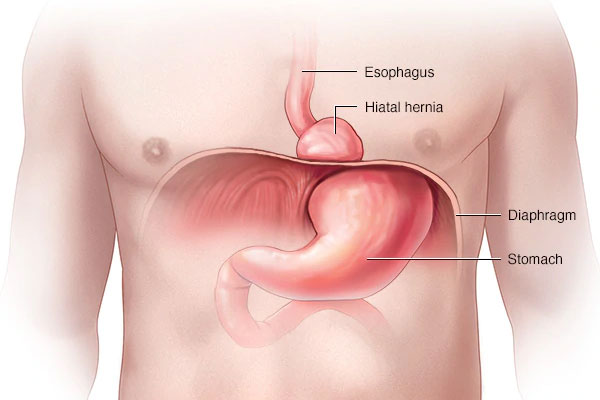
What is Hiatal Hernia?
Hernia is a common condition in which part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a defect within the muscle. Hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of stomach bulges through an opening (hiatus) within the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a large muscle, which separates your abdomen and chest.