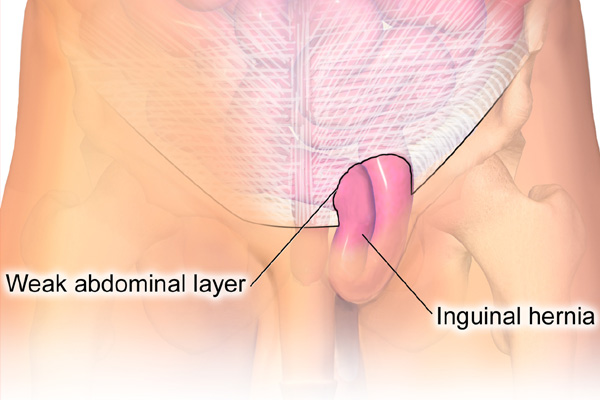
Inguinal Hernia (Groin Hernia)
A hernia is the protrusion of an organ or part of an organ through an abnormal opening usually a defect in the walls of its cavity. The inguinal hernia is the result of the protrusion of the intestine into the inguinal canal and it is mainly seen in males because the inguinal canal is the path for testicular descent in the early years.