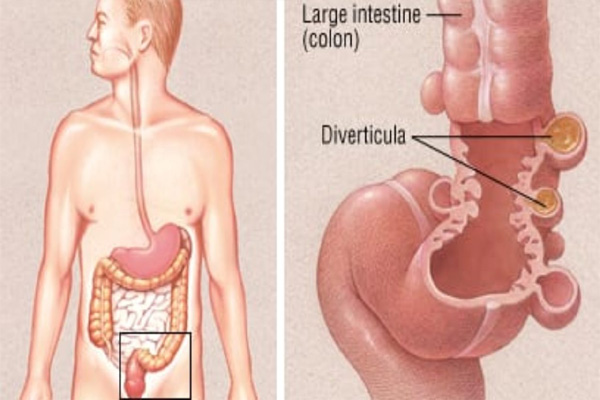
What is Diverticulitis?
A diverticulum (plural: diverticula) is a small sac or an outward pouch-like structure that is present within the large intestine. It is formed through points of weakness within the muscular wall of the intestine. Diverticulitis is a medical condition in which one or more diverticula becomes inflamed and swollen.